E-Waste Recycling Service: From Pickup to Recycling
When choosing a professional e-waste recycler you need to focus on the services offered which should include: secure pickup, certified data destruction, documented chain-of-custody tracking, responsible recycling, and clear reporting. These services will ensure business data is protected, compliance risk is reduced, and e-waste disposal becomes predictable for your business.
E-waste recycling service features
Choosing a certified vendor
When you intentionally choose a e-waste recycling company that is certified and has a controlled offloading process you ensure your data and the environment remain protected.
1. Identify Transparency
The service provider should provide transparency of tracking so you know where your equipment is, what’s being done with it, and who is handling it. Clear communication prevents and reduces risk.
2. Verify Certification
The compliance certificates for the provider should be recognized certifications like R2v3 or e-Stewards. When regulated providers provide proper handling of hazardous materials, and secure data destruction that can make audits seamless.
3. Ask for Documented Chain of Custody
The vendor should provide device tracking from pickup to final processing. When a clear chain of custody is provided the business reduces the risk of lost devices, data leaks, or compliance gaps.
4. Clear, Usable Reporting
You should receive inventory reports, certificates of data destruction, and recycling documentation. This makes audits easier and supports ESG reporting without scrambling later.
Certified vs Non-Certified E-Waste Recyclers
| Criteria |
Certified Recycler (R2v3 / e-Stewards) |
Non-Certified Recycler |
| Data destruction |
Certified wiping or shredding with documented proof |
Unverified or undocumented data handling |
| Chain of custody |
Tracked from pickup to final processing |
Limited or no visibility after pickup |
| Downstream handling |
Verified, audited processors |
Higher risk of informal or unknown processing |
| Compliance readiness |
Audit-ready reports and certificates |
Little to no usable documentation |
| Environmental controls |
Responsible recovery + landfill diversion |
Higher landfill / mishandling risk |
Quick Decision Checklist for Businesses
Before you choose an e-waste recycler, confirm these basics:
- ☐ Provides scheduled, secure e-waste pickup
- ☐ Offers certified data destruction (NIST-aligned wiping or physical destruction)
- ☐ Maintains chain-of-custody logs for every asset
- ☐ Supplies certificates of destruction and recycling
- ☐ Uses verified downstream processors (no surprises after pickup)
- ☐ Supports reuse and value recovery through IT asset liquidation when devices still have value
If a recycler can’t confidently check every box, the risk usually shifts back to your organization.
Core E-Waste Terms Explained
The best way to choose and evaluate a vendor is by understanding the key terms associated with IT assets that need to be retried. These terms provide qualifications that improve the internal process to ensure it holds up during audits.
- Device Pickup and Logistics: The time when collection is scheduled for secure transportation to a processing facility.
- On-Site vs Off-Site Processing: Data sensitive work that can be performed at your facility (on-site), or processing that happens at certified facilities (off-site).
- Secure Data Destruction: Wiping or physical destruction of storage media, with certified proof of completion. See IT data destruction services.
- Device Grading and Testing: The evaluation of the device condition to suggest reuse, resale, or recycling routes.
- Inventory Reporting and Chain-of-Custody Logs: The tracking of each device from pickup to final disposition.
- Environmental Reporting and Compliance Support: The provision of documents that outline recycling outcomes, and downstream handling for ESG and audit needs.
- Certificates of Data Destruction / Recycling: Documents used for compliance, security, and internal reporting.
- Material Recovery and Responsible Recycling: Separation of components (metals, plastics, batteries) for e-waste sustainable efforts.
- Remarketing and Value Recovery: Resale or refurbishing of devices for initial value recovery tied to IT asset disposition (ITAD).
- Parts Harvesting: Salvaging usable components to extend lifecycle and reduce waste.
A Breakdown of Professional E-Waste Services
Below are the core services a professional recycler should offer, and why each step matters for business disposal.
1) E-Waste Collection / Pick-Up Services
Pickup ensures logistics are handled for businesses, it also reduces reducing the risk of data expsoure with vendors providesing packaging guidance when needed, and transporting devices securely.
Best practice for businesses: Schedule a regular or one time pickup so equipment does not lose value.
Schedule a regular e-waste pickup
2) Responsible IT Asset Disposal (ITAD)
If you choose a vendor that does not provide a proper disposal path: with secure data handling, reuse/value recovery if possible, and certified recycling when it is truly end-of-life, then your business will have challenging audits.
ITAD disposal services businesses ask for:
3) Commercial vs Residential Disposal
Business pickups are more structured than residential disposal, which is usually about convenience. If you manage both (for example, remote employees), your recycler should support both flows without creating extra work.
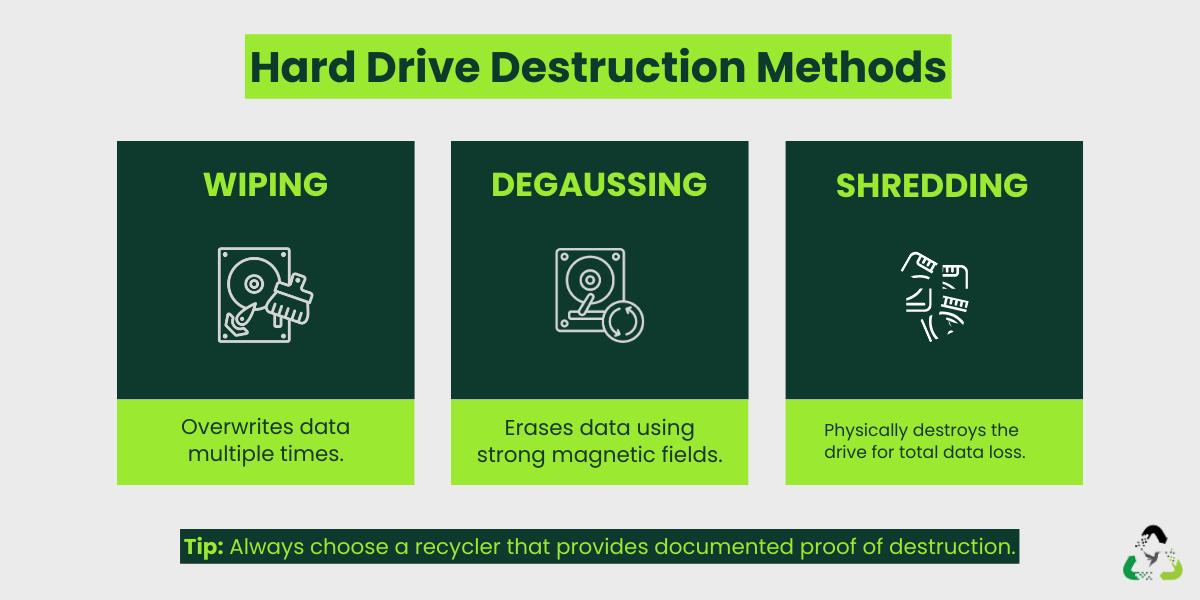
4) Data Destruction Services
Data risk is when e-waste to become a business problem. A professional recycler handles storage media first and provides proof of completion so your team can close the loop.
- Wiping: overwrites data so it cannot be recovered (best when drives are functional).
- Degaussing: uses magnetic fields to erase certain media types.
- Shredding: physical destruction for maximum assurance.
Related services: data destruction and IT data destruction services.
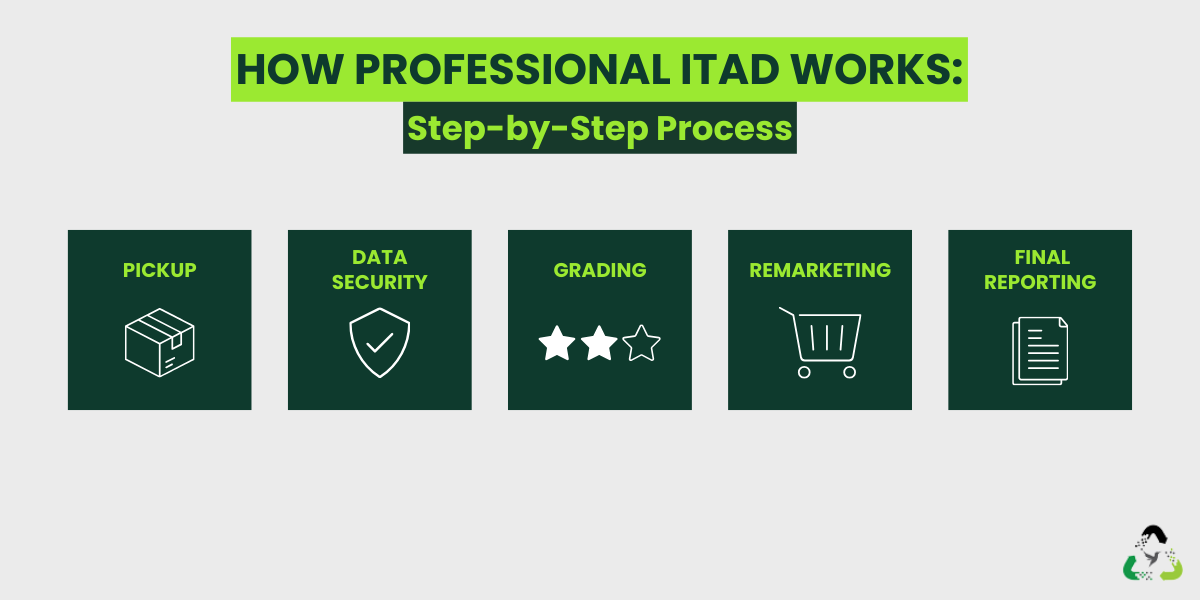
How ITAD Vendors create a Service Flow
A professional recycler will make sure all their services are connected process. From pickup to processing, each step provides a clean, traceable path for every device.
1) Pickup + Chain-of-Custody Logging
Starts with scheduled pickup. Assets are tagged and logged so nothing goes missing.
2) Data Security First
Storage media is assessed by being wiped or destroyed. Then devices move into reuse or recycling paths.
3) Grading, Testing, and Inventory Review
Devices are inspected for value so they can reused or resold and what should go to certified recycling.
4) Remarketing, Donation, or Material Recovery
Usable devices can enter value recovery streams; end-of-life equipment is dismantled for responsible material recovery.
5) Final Reporting
You receive documentation that closes the loop: chain-of-custody logs, certificates, and reporting you can actually use.
See IT Asset Recycling & ITAD Services
Buyer Checklist: What to Ask Before You Sign
If you are evaluating an ITAD partner, ask these questions.
- Can you provide chain-of-custody logs per asset?
- Do you follow NIST-aligned wiping or offer physical destruction?
- Will you share sample certificates of destruction and recycling?
- Where does material go after processing? (downstream verification)
- Do you support multi-location pickups and reverse logistics? (reverse logistics pickup)
- Can you support ITAD for large refreshes or data centers? (data center decommissioning)
- Do you offer value recovery? (IT asset liquidation)
Proper e-waste management goes beyond clearing out old devices. When pickup, data destruction, grading, value recovery, and certified recycling work together, you protect sensitive information, recover value, stay compliant, and reduce environmental impact. The process becomes simple because it is structured.
Start With Free E-Waste Pickup
FAQs
What services should an ITAD recycler offer?
A reliable recycler will cover secure data destruction, certified e-waste processing, pickup and logistics, inventory reporting, grading, remarketing/value recovery, environmental reporting, and verified downstream handling. These services ensure devices are handled safely from pickup to final disposition.
Do I need on-site hard drive shredding?
On-site shredding helps when devices have sensitive data and cannot leave the building intact. For most businesses, certified off-site wiping or shredding with a documented chain of custody is enough.
How do I verify if a recycler is certified?
Look for a compliance library and ask for proof of certification. A reputable recycler will have transparent certification details and explain their downstream handling.
Is remarketing always an option?
No, only if devices still have usable life. If the equipment is in good condition, vendors can test and grade it to resell and recover value. Older or damaged items have to go through material recovery and certified recycling.
What does a recycling certificate include?
A proper certificate typically lists what was processed, when it was processed, and confirms handling met environmental and data-security standards. It gives you documentation for compliance and audits.




Leave a Reply