For years now, plastic has dominated environmental conversations. But today, a new threat is taking the center stage, and it is on its way to becoming the fastest-growing and most toxic waste stream. E-waste is every discarded smartphone, charger, and retired laptop.
The global e-waste crisis is getting worse every day as it is driven by rapid digitalization, trending tech upgrades, and a booming demand for tech in AI. E-waste generation has been rising five times faster than documented e-waste recycling since 2010.
But there is always a silver lining; there are multiple ways of turning this global crisis into opportunities. Instead of seeing e-waste as an unavoidable byproduct of modern life, we can view it as a critical resource. In this article, we will look at some of the significant opportunities to turn e-waste crises into fruitful opportunities.
Urban Mining
Most people are unaware, but e-waste is not just trash. It is one of the richest mines on the planet. In modern electronics, you will find cobalt, gold, lithium, copper, and other rare earth elements, including palladium.

These minerals are increasingly difficult and costly to extract from otherwise traditional mines. Therefore, recovering them from e-waste is a cheat code that helps recycle these raw materials without stressing the environment.
Here are some tidbits that make urban mining all the more lucrative:
- A ton of discarded smartphones can contain significantly more gold than a ton of ore from a typical gold mine.
- Urban mining helps reduce demand for unethical labor conditions when mining naturally.
- The recovered materials can be used directly to produce new electronics, such as EV batteries and other clean energy technologies.
| Factor | Traditional Mining | Urban Mining (E-Waste Recovery) |
|
Source of Materials |
Ore extracted from the earth | Metals recovered from old electronics |
|
Environmental Impact |
High. Habitat destruction, pollution, and carbon emissions | Low. No land disruption, reduced emissions |
|
Energy Requirements |
Very high | Up to 80% lower |
|
Labor Conditions |
Often unsafe, sometimes linked to conflict minerals | Skilled, regulated recycling jobs |
|
Yield of Precious Metals |
Low (e.g., ~5–6g of gold per ton) | Exceptionally high (hundreds of grams per ton of e-waste) |
Urban mining is not just theoretical anymore. Researchers and innovators have proven that closed-loop recycling systems can be profitable and sustainable.
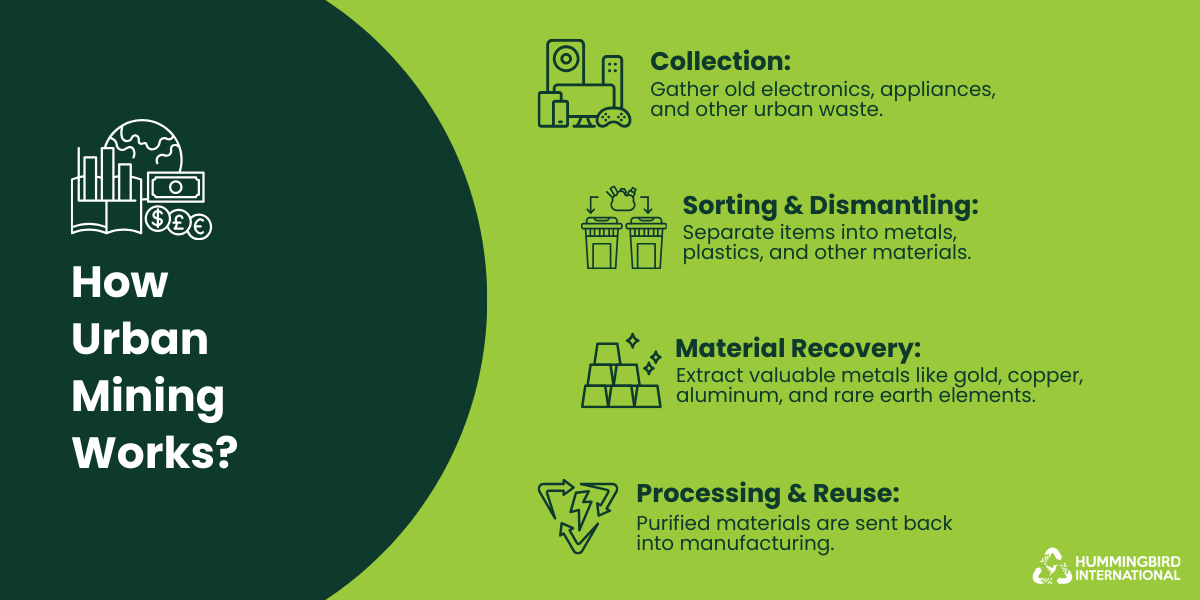
But to ensure the best outcomes, you must partner with responsible e-waste recyclers such as Hummingbird International. Doing so will ensure that all raw materials are recovered safely and no toxins end up in landfills.
IT Asset Disposal
Since organizations are modernizing, a new opportunity is peaking through. Unlocking value from devices no longer in use is now a possibility led by the ITAD industry. Old hardware or e-waste is no longer viewed as a liability. It is an asset and has several layers of value.
Here is how ITAD can convert E-waste into an opportunity you shouldn’t overlook:
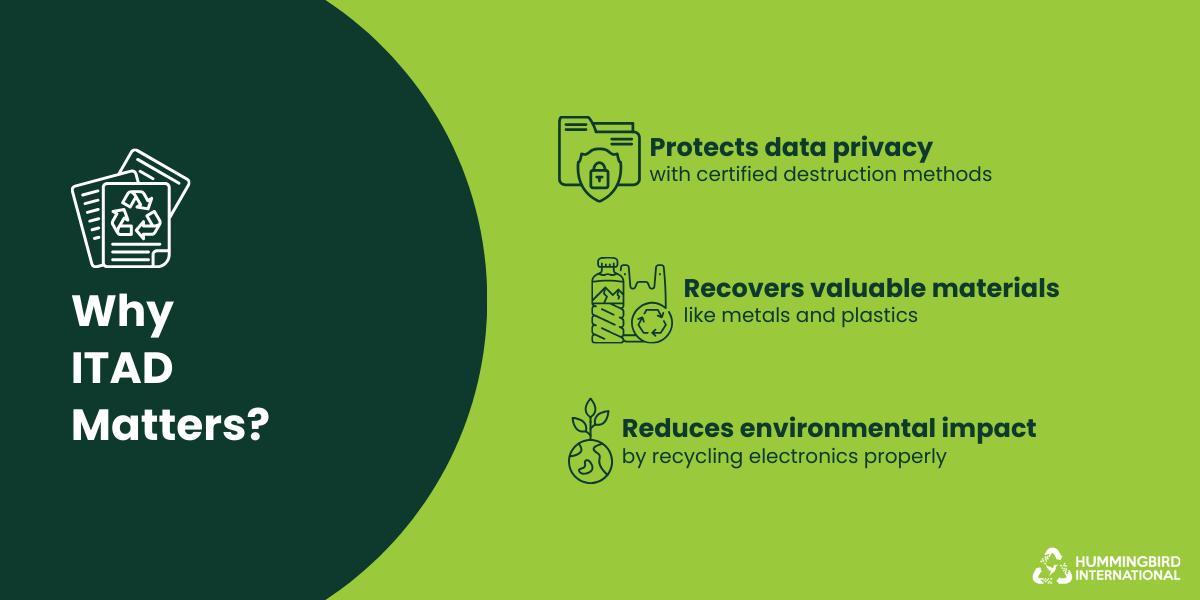
- With ITAD data destruction, companies can prevent data breaches, protect their brand image, and ensure compliance.
- By removing old data, these devices can be refurbished and repaired, extending their life and creating a secondary market for the hardware.
Cybersecurity risks are increasing by the minute, and companies are now investing in ITAD not just to avoid problems but also to gain strategic advantages. With ITAD, you can turn retired devices into recoverable revenue and reduce operational costs by extending their lifespans.
The ITAD sector is paving the way for a circular tech economy, so instead of retiring devices, you can reuse them or use the revenue from resale to get new, better tech.
Bridging The Digital Divide
Even though technology is advancing at lightning speed, many people still lack basic access to devices like smartphones and laptops. It is important to understand that tech is not a luxury, but it is a prerequisite for education, making an income, and being a part of the global economy. But refurbishing can be a lifeline for these underserved economies.

By repairing, reusing, and donating older but functional electronics, we can reduce the great divide.
Here are some practical examples of its impact:
- Equip schools and learning centers with affordable laptops and tablets
- Provide job seekers with the tools needed to apply for work or learn new skills
- Support small businesses and entrepreneurs in underserved regions
- Increase women’s digital access, narrowing the gender gap that still limits economic mobility
- Connect rural communities that lack access to modern hardware
- Strengthen nonprofits and community organizations that rely on donated devices
A single laptop can enable a student’s education, improve a family’s connection to their loved ones abroad, and even provide online income avenues.
Silver Lining Of E-Waste
The e-waste crisis is real, which makes the opportunities relating to it also real. Therefore, by embracing opportunities such as urban mining, ITAD services, and device reuse. We can now shift from a take, make, and waste economy to a circular technology economy that protects the planet, boosts economies, and supports communities.

Simple advice from our experts at Hummingbird International would be to:
- Use your devices longer
- Repair them rather than replacing them
- Ensure proper data destruction
Hummingbird International offers secure IT asset disposal, and all you have to do is get in touch with our team. Recycle, reduce, and reuse with Hummingbird International.
FAQs
Is urban mining actually profitable?
Yes, Urban mining is actually profitable when done at scale, and with proper processes, it can generate revenue through the recovery of high-value materials.
What is ITAD, and why is it important?
IT Asset Disposition is the process of securely retiring hardware. It includes data destruction, refurbishment, resale, recycling, and compliance documentation. It can protect businesses from data breaches and loss of trust.
Can ITAD and urban mining create jobs?
Yes, both sectors can create skilled jobs, such as sorting electronics, dismantling, recycling, and refurbishment, which will, in turn, support local economies.
Is urban mining limited to electronics?
Urban mining is not limited to electronics; it also recovers valuable metals from batteries, appliances, and vehicles that contain rare or recyclable materials.
How can I help bridge the digital divide?
By donating functional electronics and repairing old devices can provide technology access to underserved communities, students and even small businesses.


Leave a Reply