- What Is Recycling?
- What Is Refusing?
- How Recycling Transforms End-of-Life Electronics
- How Refusing New Purchases Shapes Your IT Footprint
- Decision Matrix: When to Recycle, Reuse, Repair, or Refuse Purchase
- Why This Choice Matters for Organizations
- How to Set Up a Practical Electronics Lifecycle Policy
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
- 1. How can an organization decide whether to repair, reuse, or recycle aging electronics?
- 2. What equipment signs indicate that recycling is the only safe option?
- 3. How can organizations prevent unnecessary e-waste during IT refresh cycles?
- 4. What certifications should companies look for when selecting an e-waste recycler?
What Is Recycling?
Recycling deals with equipment that has reached the end of its working life or no longer meets safety, compliance, or data-handling standards. Devices are dismantled so metals, plastics, and circuit components can be recovered and fed back into manufacturing instead of ending up in landfills.
- Supports environmental reporting and ESG targets
- Ensures controlled destruction of drives and memory modules
- Reduces raw material demand for future hardware production
What Is Refusing?
Refusing is the practice of stopping a purchase before it starts. It means challenging the assumption that “new is better” and looking for alternatives across the organization. This helps control e-waste at its source and encourages teams to plan around shared resources instead of siloed buying.
- Prevents unnecessary asset growth and storage clutter
- Encourages device pools, equipment libraries, or cloud-first workflows
- Strengthens procurement discipline and reduces impulse upgrades
Before we move ahead, here’s a glossary of useful terms that you might encounter during the decision matrix:
- Recycle: Breaking down unusable electronics so their materials can be recovered.
- Refuse: Declining new purchases when needs can be met through existing tools.
- Repair: Fixing hardware issues so the device can continue its normal role.
- Reuse: Moving a device to another team or task that requires less performance.
- Asset Lifecycle: The full journey of a device from purchase to retirement.
- Asset Audit: A scheduled check of all hardware to measure condition, performance, and remaining lifecycle.
- Device Retirement: The formal process of removing equipment from service, including data wiping and documentation.
- End-of-Life (EOL): A stage where a manufacturer stops supporting updates, patches, or parts for a device.
- Right-to-Repair: The principle that users should be able to fix their equipment without barriers.
- Circular Economy: A system where products and materials are kept in use for as long as possible.
- E-waste: Discarded electronics that require responsible handling.
- IT Refresh Cycle: Scheduled replacement planned by an organization’s technology team.
- Material Recovery: Extracting metals, plastics, and components from dismantled electronics.
- IT Asset Disposition (ITAD): Professional services that manage secure removal, recycling, or resale of electronics.
- Lifecycle Planning: Forecasting when devices need maintenance, upgrades, or replacement to avoid surprise failures.
- Operational Fit: Evaluating whether a device still aligns with the workload it is assigned to.
- Salvage Value: The remaining value a device holds before being recycled or dismantled.
- Waste Minimization: A policy goal focused on reducing the total volume of discarded electronics from an organization.
How Recycling Transforms End-of-Life Electronics
Here’s what happens when you choose to follow a streamlined computer recycling process.
Environmental Protection and Resource Recovery
Recycling electronics keeps hazardous materials out of landfills and recovers valuable resources instead of letting them go to waste. Certified recyclers dismantle devices and extract metals, plastics, and other materials for reuse.
- Prevents toxic substances (like lead, mercury, cadmium) from contaminating soil and water.
- Reduces demand for new raw materials — cuts down harmful mining and conserves scarce resources such as copper, gold, and silver.
- Decreases energy use and greenhouse gas emissions compared to manufacturing from virgin materials.
Data Security and Compliance
Old devices often hold sensitive business data. Recycling via certified providers ensures safe data destruction.
- Secure wiping, degaussing, or shredding to get rid of personal data protects against breaches.
- Helps meet regulatory requirements and avoid fines or legal liability tied to improper disposal.
Cost Efficiency and Potential Value Recovery
Recycling can help reduce the costs associated with storing or disposing of outdated equipment — and sometimes recoup value from recovered materials.
- Avoid ongoing storage or disposal overhead for outdated hardware.
- Possible revenue or credit through resale or recovery of valuable components.
- More predictable asset-lifecycle management, reducing financial surprises tied to bulk disposal or disposal fines.
Reputation, Sustainability, and Corporate Responsibility
Adopting proper recycling practices reflects well on a company’s commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
- Strengthens environmental and social credentials — practical for ESG (environmental/social /governance) reporting or stakeholder communications.
- Builds trust with customers, partners, regulators, investors, and internal stakeholders who value ethical and responsible behavior.
How Refusing New Purchases Shapes Your IT Footprint
Saying no to buying new equipment comes with plenty of perks, including:

Cost Control and Reduced Capital Expenditure
Refusing to purchase new gear when existing assets suffice helps keep budgets under control.
- Avoids unnecessary capital outlay for hardware that isn’t strictly required.
- Lowers the total cost of ownership by maximizing the use of current equipment.
- Forces more strategic thinking about actual business needs, not wants.
Waste Reduction and Environmental Benefit
By not adding more devices to the fleet, you reduce the eventual e-waste burden.
- Slows the growth of the e-waste volume your organization generates.
- Less demand for manufacturing new devices indirectly reduces resource extraction and carbon footprint.
- Encourages longer device lifecycles, which aligns with sustainability and circular-economy principles.
Encourages Responsible Use and Efficient Asset Management
Refusal pushes teams to optimize what they have, which can lead to smarter policies and operations.
- Promotes reuse, reassignment, or redistribution of current devices instead of “buy-and-discard.”
- Reduces clutter and storage burden of underutilized or redundant equipment.
- Helps instill a culture of mindful consumption rather than habitual replacement.
Supports Strategic Planning and Procurement Discipline
A refusal-favoring stance forces clearer justification before buying more gear.
- Encourages proper assessment of actual need, workload demands, and resource utilization before procurement.
- Discourages impulse upgrades driven by novelty rather than necessity.
- Helps keep asset-lifecycle planning disciplined — particularly valuable in large organizations managing many devices.
Decision Matrix: When to Recycle, Reuse, Repair, or Refuse Purchase
Organizations often face different scenarios as equipment ages or needs change. This decision framework helps evaluate whether a device should be repaired, reused elsewhere, recycled, or simply not replaced with new gear. The goal is to balance:
- Cost
- Performance needs
- Compliance
- Environmental responsibility
Below is a simplified lifecycle flow to show decision points, followed by detailed guidance.
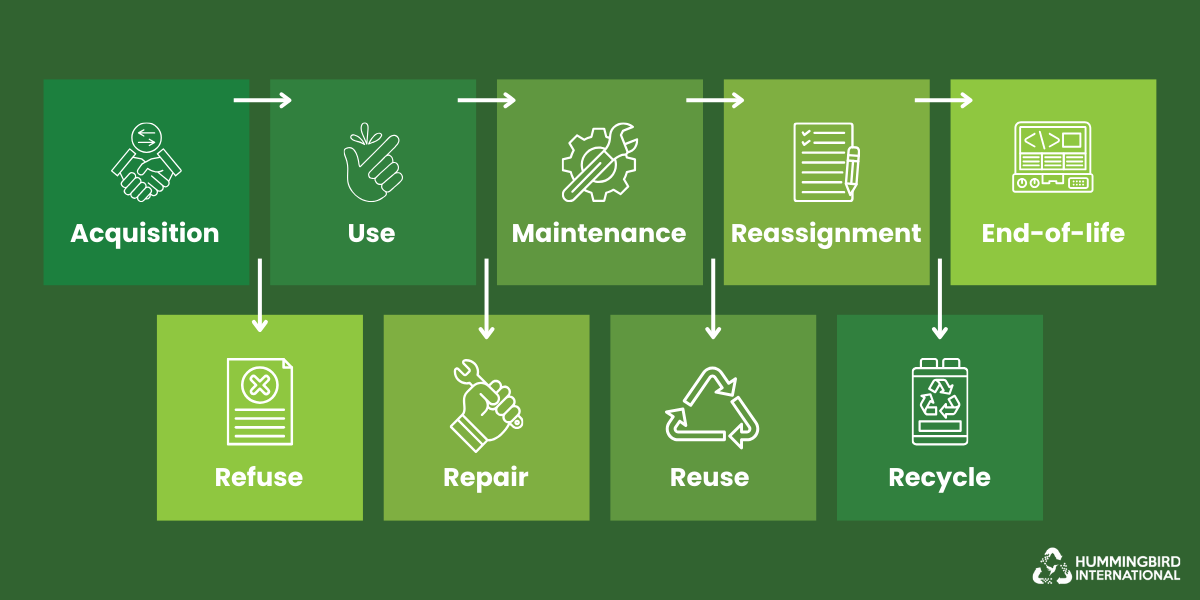
1. Repair / Maintain
When it makes sense to bring a device back to acceptable performance rather than discard it.
Repair is suitable when faults are minor, spare parts or maintenance remain affordable, and performance still meets current business needs. Extending usable life can delay new procurement and reduce waste.
Consider repair when:
- Hardware failure involves replaceable components (e.g., a defective power supply, broken fan, upgradeable memory, or storage).
- The repair cost is low compared to the replacement cost.
- Device still meets performance, security, and compatibility requirements.
Benefits include:
- Lower capital expenditure than buying new gear.
- Slower accumulation of redundant hardware.
- Reduction in environmental burden by delaying new manufacturing.
In fact, studies show that careful maintenance and selective upgrades can extend equipment life by 2–3 years for many items — saving organizations significant replacement costs while reducing waste.
2. Reuse (Internal Reassignment / Light-duty Use)
Even if a device is too weak for its original heavy workload, it may still serve well in lighter roles — for example, for admin tasks, guest use, training, or as backup machines.
Reuse makes sense when:
- Performance no longer matches core workloads, but the device still operates reliably.
- Security, compliance, and data-wiping requirements are met.
- There’s a real internal need elsewhere (instead of buying new).
Advantages include:
- Reduces procurement pressure and budget demands.
- Extends the lifecycle of hardware, aligning with circular-economy principles.
- Minimizes idle equipment and storage burden.
Reuse helps organizations squeeze more value out of existing assets before considering disposal or replacement.
Recycle (End-of-Life Disposal / Material Recovery)
When hardware is obsolete, irreparable, unsafe, or no longer meets compliance/security standards, recycling becomes the responsible choice.
Recycling involves sending devices to certified recyclers who dismantle hardware, extract metals, plastics, and other materials, and ensure safe disposal of hazardous components.
Main reasons to recycle:
- The device cannot be fixed, or it is financially impractical to repair.
- Component or design is obsolete — e.g., lack of spare parts, incompatible with current infrastructure, or security vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory or environmental compliance demands safe disposal.
Global data highlight the urgency: in 2022, around 62 billion kg of e-waste was generated worldwide, yet only about 22.3% of that was formally collected and recycled.
Proper recycling recovers valuable materials (metals, plastics) and avoids environmental hazards from landfill or informal disposal. Organizations should prefer certified recyclers to ensure safe handling, data security, and traceability.
Refuse Purchase (Decline New Gear / Extend Current Assets)
Refusing a new purchase means actively deciding not to replace or upgrade equipment — leveraging existing assets, shared resources, or alternative solutions instead.
This approach may apply when:
- Existing hardware or infrastructure still suffices for workload demands.
- Planned upgrades are not justified by performance or business benefit.
- Preference is given to reuse, minimalism, or sustainability objectives.
Refusing unnecessary purchase offers benefits:
- Controls capital expenditure and reduces procurement overhead.
- Suppresses the growth of e-waste generation.
- Encourages careful planning, efficient use of resources, and avoids redundancy.
This approach aligns with a circular-economy mindset and supports long-term sustainability and fiscal discipline.
To make the decision process easier to apply in real situations, the following table maps common conditions to the right action.
| Condition | Action |
| If the hardware fault is minor and the repair cost is modest compared to replacement | Repair / Maintain |
| If the device no longer meets primary workload needs, but remains functional and secure | Reuse (internal reassignment or lighter duties) |
| If the device is irreparable, unsafe, outdated, or fails compliance/security standards | Recycle (through certified disposal) |
| If a new purchase request arrives, but existing assets suffice, or demand is unclear | Refuse purchase |
| If support or maintenance costs exceed a defined threshold relative to replacement cost | Recycle or plan a proactive upgrade |
| If workload demands can be met via virtualization, shared resources, or alternative solutions | Refuse purchase, or reuse |
Why This Choice Matters for Organizations
Making the right decision about what to do with aging electronics affects more than just the IT department. Each choice carries implications for budgets, compliance, data security, and corporate reputation.
-
Impact on Procurement Budgets
Deciding to repair, reuse, or refuse new purchases can significantly reduce capital expenditure. Extending the lifecycle of existing equipment delays costly upgrades and lowers the total cost of ownership.
-
Compliance with Environmental Standards
Proper recycling ensures organizations meet environmental regulations and reporting requirements. Certified disposal prevents fines and demonstrates responsible management of hazardous e-waste.
-
Data Security Considerations
Devices often store sensitive business information. Choosing certified recyclers or secure data-wiping methods prevents breaches and protects organizational data during end-of-life processes.
-
Reputation and Sustainability Commitments
Responsible lifecycle management reflects an organization’s dedication to sustainability. It strengthens ESG reporting, builds trust with stakeholders, and enhances public perception of corporate responsibility.
How to Set Up a Practical Electronics Lifecycle Policy
Once the decision matrix is in place, the next step is to turn those ideas into a working policy that the whole organization can follow. A clear policy keeps choices consistent across departments and prevents ad-hoc decisions that lead to waste, unnecessary spending, or compliance gaps.
1. Set Clear Decision Thresholds
Before teams can act with confidence, they need defined criteria. Thresholds give everyone a shared understanding of what counts as repair-worthy, what signals end-of-life, and what warrants a new purchase.
Use thresholds for:
- Cost (for example, repairs capped at a percentage of replacement cost)
- Minimum performance standards
- Safety or compliance flags
- Energy efficiency or environmental impact, where relevant
These markers prevent subjective decisions and help standardize choices across departments.
2. Assign Roles and Approvals
Clear roles keep the policy running smoothly. Each stage of the lifecycle should sit with the right decision-maker.
Typical responsibilities may include:
- IT team: technical assessment, repair feasibility, performance evaluation
- Procurement: purchase approvals, cost reviews, vendor coordination
- Sustainability office or compliance lead: recycling standards, certification checks, reporting
- Department heads: validating business need for replacement or upgrade
This separation keeps decisions fair and reduces unnecessary spending.
3. Create Routine Review Cycles
Policies work best when they evolve. Regular audits ensure equipment remains fit for purpose and reduce surprises during refresh cycles.
A review cycle may cover:
- Annual or semi-annual hardware audits
- Performance checks tied to workload changes
- Data security reviews for aging devices
- Scheduled updates to thresholds as technology prices shift
These touchpoints help teams spot issues early rather than reacting when equipment fails.
4. Document Disposal and Recycling Standards
End-of-life disposal must be handled with care. Every organization should have a simple, well-documented process that keeps data safe and prevents equipment from entering informal e-waste streams.
Documentation should include:
- Approved recycling partners and their certifications
- Data-destruction methods required before equipment leaves the building
- Material handling rules for batteries, monitors, and hazardous components
- Chain-of-custody steps for compliance reporting
This protects the organization legally and environmentally, while making the recycling process seamless from request to completion.
Final Thoughts
Managing aging electronics wisely can save money, reduce e-waste, and protect sensitive data. By following a clear repair, reuse, recycle, or refuse policy, organizations can extend device lifecycles and meet sustainability goals. Hummingbird International LLC supports businesses throughout this process, offering secure, certified IT asset recovery that keeps both operations and the environment safe. Ready to take action?
FAQs
1. How can an organization decide whether to repair, reuse, or recycle aging electronics?
An organization can make this decision by assessing three things:
-
a) The device’s condition.
-
b) The cost of restoring it.
-
c) Whether it still meets current operational or security standards.
If a minor fix restores acceptable performance, repair makes sense. If the device is too weak for its original role but still reliable, it can be reassigned for lighter tasks. If it is unsafe, obsolete, or fails compliance checks, recycling through a certified provider becomes the responsible outcome.
2. What equipment signs indicate that recycling is the only safe option?
Recycling becomes the safest choice when a device is physically damaged, cannot pass data-security or compliance checks, lacks available spare parts, or poses electrical or safety risks. Devices that can no longer support required software or security updates should also be routed to certified recycling.
3. How can organizations prevent unnecessary e-waste during IT refresh cycles?
Organizations can reduce unnecessary e-waste by planning refresh cycles around actual performance needs, reassigning still-usable devices, and refusing new purchases unless workloads truly require them. Audits, repair evaluations, and internal reuse programs keep equipment in service longer and limit premature disposal.
4. What certifications should companies look for when selecting an e-waste recycler?
Companies should rely on recyclers that follow verified, traceable standards. The most recognized certifications include:
- R2 (Responsible Recycling)
- e-Stewards Certification
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management
- NAID AAA for data security and destruction


Leave a Reply