- 1. Infographic on DIY E-Waste Project Ideas
- 2. Infographic on 8 Eco-Conscious Practices for Green Businesses
- 3. Infographic on Ethical E-Waste Recycling
- 4. Infographic on E-Waste: A Colossal Problem in the United States
- 5. Infographic on E-Waste: The World in Jeopardy
- 6. Infographic on How Much Are We Wasting
- 7. Infographic on 10 Benefits of Recycling E-Waste
- 8. Infographic on Recycling by the Numbers
- 9. Infographic on the 10 Most Alarming Recycling Statistics in 2022
- 10. Infographic on the Route of the Common Gadget
- 11. Infographic on 6 Tips to Prevent Waste
- 12. Infographic on Where Is All the E-Waste Going?
- 13. Infographic on E-Waste: The World Drowning in Cables and Devices
- Summing Up
1. Infographic on DIY E-Waste Project Ideas

This infographic introduces the idea of reusing discarded electronics through simple DIY projects. It includes tips for both skilled and non-skilled DIYers to convert old devices and components into functional tools, creative builds, or learning projects, rather than letting them become waste.
Key Insights
- DIY projects keep e-waste out of landfills and give old junk a new purpose.
- Electronic parts can be used to build DIY projects, including automated cat feeders and beat-bearing rhythm sequencers.
- E-waste can be reused in a variety of art forms as well—sculptures (by combining motherboards, chips, cables, etc.) or unique wall art (e-waste mounted on canvas).
2. Infographic on 8 Eco-Conscious Practices for Green Businesses
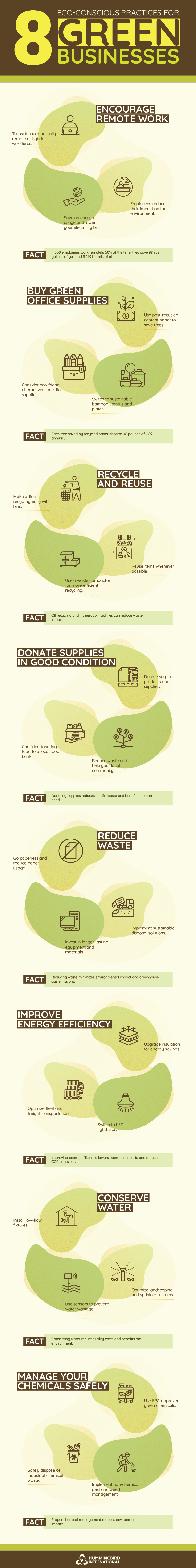
Many organizations have started rethinking how they use energy, manage waste, and source materials, especially in the years following the pandemic. Companies such as Tesla, Samsung, and Panasonic have shown that sustainability works best when it is built into daily operations rather than treated as a side initiative. This infographic focuses on how businesses can reduce environmental strain through practical, everyday decisions.
Key Insights
These actions focus on reducing waste, improving efficiency, and encouraging mindful use of resources. Together, they create a more sustainable workplace while supporting long-term environmental goals.
- Encourage remote work
- Buy green office supplies
- Recycle and reuse
- Donate supplies in good condition
- Reduce waste
- Improve energy efficiency
- Conserve water
- Manage your chemicals safely
3. Infographic on Ethical E-Waste Recycling

This infographic explains why ethical e-waste recycling has become a pressing issue rather than a future goal. It focuses on the growing urgency around ethical e-waste recycling and why existing systems are falling short. While regulations have expanded over the years, progress has been slow, and ethical sustainability remains absent from many recycling practices.
Key Insights
- Ethical e-waste recycling focuses on disposing of electronics in ways that protect people, prevent environmental harm, and ensure hazardous materials are handled safely.
- The volume of e-waste is rising faster than responsible systems can manage it, making delays and half-measures increasingly damaging.
- Important considerations include responsible disposal, proper handling, compliance with regulations, sustainable practices, data security, and trust and accountability.
4. Infographic on E-Waste: A Colossal Problem in the United States
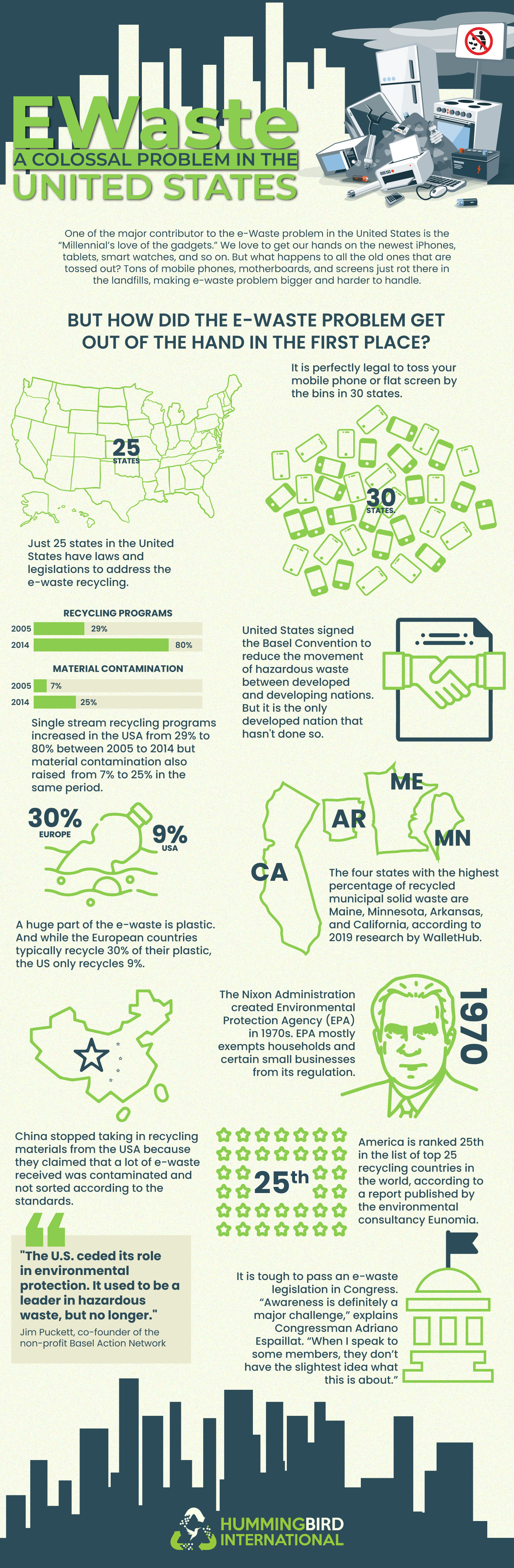
This infographic breaks down how the e-waste problem in the United States grew so quickly and why it has become so difficult to manage. It looks at consumption patterns, weak and uneven recycling laws, and how convenience often outweighs responsible disposal. The visual also highlights how much e-waste the U.S. generates, how little is properly recycled, and where gaps in regulation continue to hold progress back.
Key Insights
- The US generates massive amounts of e-waste each year, driven by short device lifecycles and constant upgrades.
- Only a fraction of discarded electronics are recycled, with most ending up in landfills or informal channels.
- E-waste laws vary by state, creating inconsistent enforcement and uneven recycling outcomes.
- Consumer awareness and access to recycling programs remain limited in many regions.
- Without stronger systems and accountability, the problem continues to scale faster than solutions.
5. Infographic on E-Waste: The World in Jeopardy
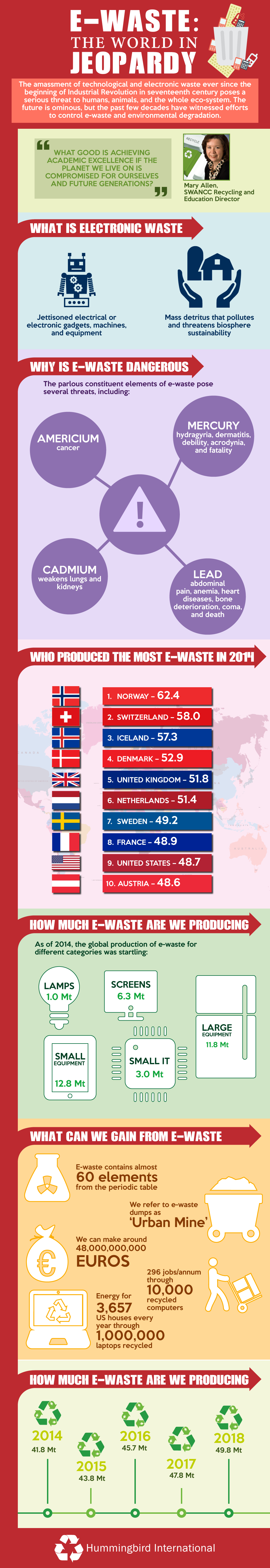
This infographic takes a global view of the e-waste crisis and shows how rapidly discarded electronics are piling up across countries. It explains what counts as electronic waste, why it is dangerous, and which regions generate the most of it. The visual also highlights how much value is locked inside e-waste and what the world stands to lose when electronics are dumped or burned instead of properly recycled.
Key Insights
- In 2019 alone, the world generated over 50 million metric tons of e-waste, with only a small share formally recycled.
- Countries like Norway, Switzerland, and the UK ranked among the highest e-waste producers per capita that year.
- Toxic materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and americium make e-waste hazardous to human health.
- One million recycled laptops can save enough energy to power 3,657 homes for a year.
- E-waste contains valuable metals, with every ton holding significantly more gold than mined gold ore.
6. Infographic on How Much Are We Wasting

This infographic looks at how much electronic waste we generate, what qualifies as e-waste, and where it actually ends up. It breaks down common devices people discard every year and highlights how quickly waste piles up when electronics are replaced instead of reused or recycled. The visual also connects everyday consumption habits with the environmental and resource costs behind discarded electronics.
Key Insights
- E-waste includes everyday items like cellphones, laptops, TVs, printers, DVD players, and desktop computers.
- The world generates 20 to 50 million metric tons of e-waste every year, with numbers rising steadily.
- Each person discards roughly 45 to 125 pounds of electronic waste annually.
- Only about 20% of global e-waste is recycled properly, leaving most mismanaged.
- E-waste contains hazardous materials, but also valuable resources that are lost when devices are dumped instead of recovered.
7. Infographic on 10 Benefits of Recycling E-Waste

This infographic focuses on the practical and measurable benefits of recycling electronic waste instead of sending it to landfills. It shows how proper e-waste recycling supports the environment, strengthens the economy, and reduces resource loss. From cutting emissions to saving energy and creating jobs, the visual lays out why recycling electronics delivers value far beyond simple disposal.
Key Insights
- Recycling e-waste can save 160,000 cubic meters of landfill space, easing long-term waste pressure.
- Proper recycling helps prevent 23,000 tons of greenhouse gas emissions.
- E-waste recycling could create 2.3 million jobs by 2030, supporting economic growth.
- Recovering metals through recycling saves up to 74% of the energy needed to produce them from raw materials.
- Recycling electronics generates financial value through cost savings, tax revenue, and resale of usable devices.
8. Infographic on Recycling by the Numbers

This visual highlights the significant impact of recycling on the environment, economy, and resource management. It presents various statistics to show how recycling conserves natural resources, reduces waste, and supports employment in the recycling industry. By illustrating both environmental and economic benefits, the infographic emphasizes why recycling is essential and how individual and collective efforts contribute to a sustainable future.
Key Insights
- 544,000 trees can be saved if one roll of fiber paper towels is replaced with 100% recycled ones.
- 20 million tons of waste are thrown away annually; one ton of discarded computers contains more gold than 17 tons of mined gold ore.
- 315 kg of CO₂ emissions are avoided for every metric ton of glass used to create new products.
- 160 billion dollars’ worth of global recycling industry employment supports more than 1.5 million people.
- 79 million tons of waste material are diverted from disposal through recycling and composting, saving 9 cubic yards of space per ton of cardboard, with 98% of glass bottles returned for reuse.
9. Infographic on the 10 Most Alarming Recycling Statistics in 2022
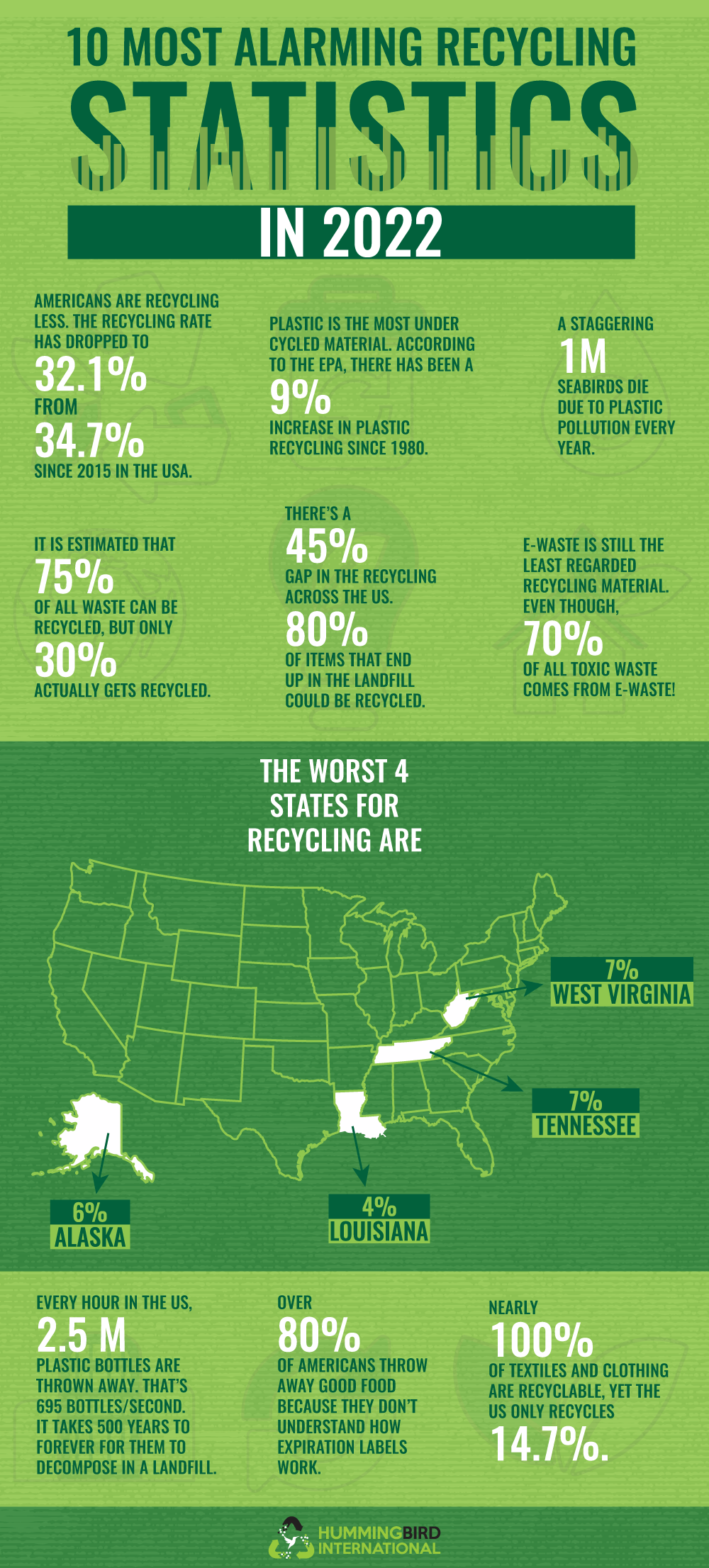
This infographic highlights the harsh reality of recycling in 2022, revealing how much recyclable waste still ends up in landfills. It sheds light on declining recycling rates, the growing plastic and e-waste problem, and the environmental damage caused by poor recycling habits. The data make it clear that despite awareness, recycling efforts are falling short across the U.S. Overall, it’s a wake-up call about how urgent better recycling systems have become.
Key Insights
- 75% of total waste is recyclable, yet only 30% actually gets recycled, showing a massive efficiency gap.
- Plastic recycling remains alarmingly low, with only a 9% increase since 1980, while plastic pollution kills 1 million seabirds every year.
- E-waste is the fastest-growing waste stream, contributing to 70% of all toxic waste, despite most of it being recyclable.
- Nearly 100% of IT waste can be recycled, but just 14.7% is properly processed.
- Recycling rates vary widely, with states like Louisiana (4%) and Alaska (6%) ranking among the worst.
10. Infographic on the Route of the Common Gadget
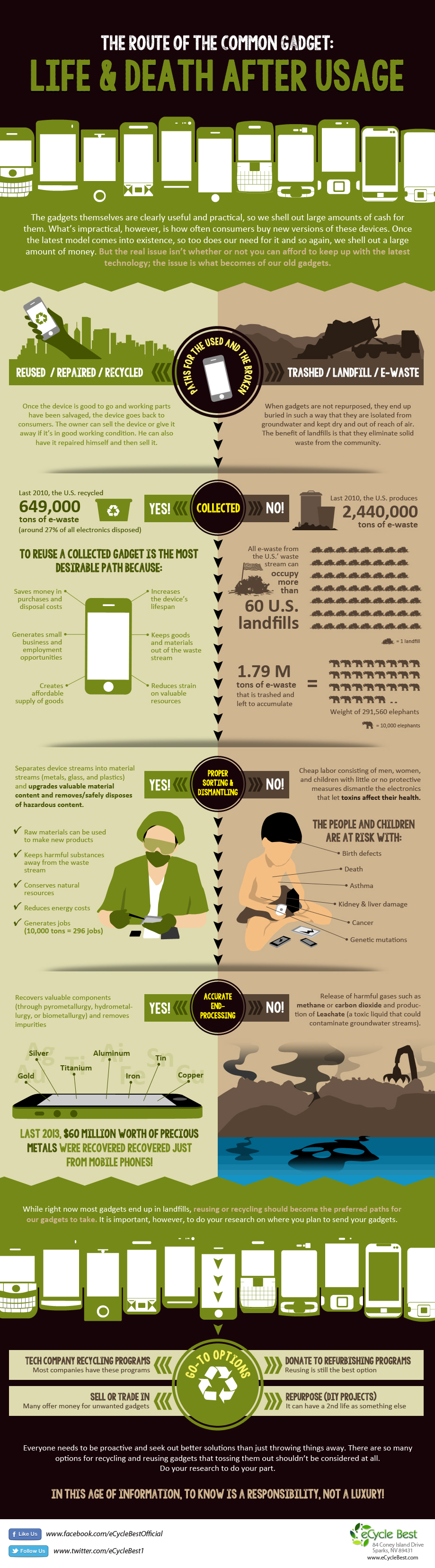
This infographic walks through the life cycle of a common electronic gadget after it’s discarded. It shows the different paths a device can take—reuse, refurbishment, recycling, or landfill—and how each choice affects the environment. Visualizing the “life and death” of gadgets, it highlights how small consumer decisions can have long-term environmental consequences. The goal is to encourage more responsible e-waste handling.
Key Insights
- Many discarded gadgets are still repairable or reusable, yet they’re often thrown away due to a lack of awareness or convenience.
- When devices aren’t properly collected, they end up in landfills where toxic materials leak into soil and water.
- Recycling and refurbishment extend a device’s life, reducing the need for new raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing.
- Consumer behavior plays a major role—choosing certified recycling or reuse channels can significantly cut e-waste impact.
- The infographic reinforces that e-waste isn’t just trash, but a resource that can be recovered if handled responsibly.
11. Infographic on 6 Tips to Prevent Waste

This infographic focuses on simple, everyday actions people can take to prevent waste before it’s even created. Instead of relying solely on recycling, it promotes waste prevention through smarter consumption, reuse, and composting. The visual breaks down practical habits that reduce household waste and encourage more sustainable living. Overall, it reinforces the idea that preventing waste is more effective than managing it later.
Key Insights
- Food waste reduction starts with small steps, like storing fruits and vegetables properly to extend freshness.
- Recycling paper products, such as newspapers, helps reduce landfill waste but works best when paired with reduced consumption.
- Reusing containers and packaging cuts down on single-use plastics and unnecessary disposables.
- Composting at home turns food scraps into valuable nutrients instead of landfill waste.
- The visual highlights that prevention comes first, with recycling as a supporting step—not the primary solution.
12. Infographic on Where Is All the E-Waste Going?

This infographic explores what actually happens to e-waste after it’s discarded and where it ends up globally. It highlights the hidden journey of electronic waste, showing how much of it is exported, improperly handled, or dumped in landfills. The visual also sheds light on the environmental and health risks caused by toxic materials in e-waste. Overall, it exposes the gap between responsible disposal and the reality of global e-waste management.
Key Insights
- Only a small portion of e-waste is properly recycled, with the U.S. recycling just 15–20% of its total electronic waste.
- A large share of e-waste is exported overseas, often to developing regions where environmental regulations are weak.
- Asia receives the majority of the world’s e-waste, placing a heavy burden on local communities and ecosystems.
- E-waste contains toxic substances like lead and mercury, which can cause long-term soil, water, and health damage when dumped.
- The infographic emphasizes that consumer awareness and stricter regulations are critical to reducing unsafe e-waste disposal.
13. Infographic on E-Waste: The World Drowning in Cables and Devices
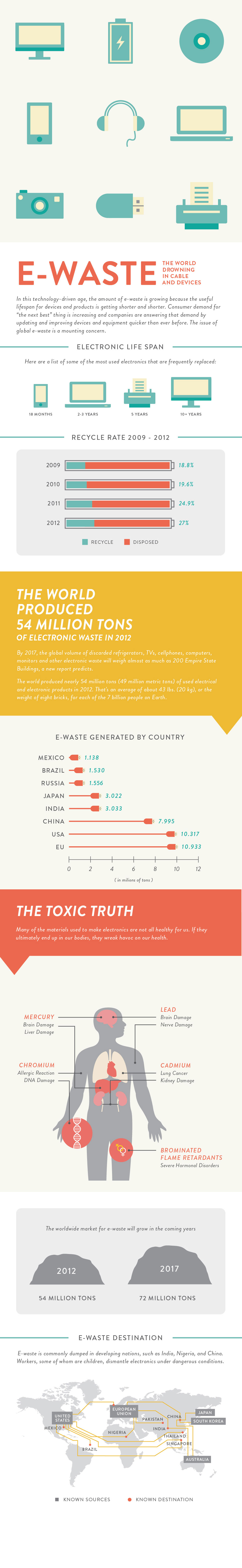
This visual focuses on the rapid growth of e-waste and how the world is becoming overwhelmed by discarded cables, devices, and electronic accessories. It illustrates the sheer volume of electronics produced and thrown away each year, along with the environmental and health risks tied to improper disposal. Connecting everyday gadgets to global waste trends, it shows how modern consumption is accelerating the e-waste crisis. The infographic ultimately calls attention to the urgent need for responsible recycling and reuse.
Key Insights
- The world generates tens of millions of tons of e-waste annually, driven by shorter device lifecycles and constant upgrades.
- Everyday items like chargers, cables, and small electronics make up a significant share of discarded tech, often overlooked in recycling efforts.
- E-waste contains hazardous materials that can harm human organs and ecosystems when not properly handled.
- Recycling rates continue to lag behind production, causing a growing gap between e-waste created and e-waste responsibly processed.
- The infographic reinforces that circular practices—repair, reuse, and recycling—are essential to slowing the global e-waste overload.
Summing Up
E-waste is a global challenge that affects the environment, the economy, and human health. These infographics reveal the scale and impact of the problem, showing why responsible disposal, reuse, and recycling are crucial. By making informed choices, both individuals and businesses can reduce waste and protect the planet.


Leave a Reply