It is hard to manage electronic waste when organizations have multiple offices, in different cities, or regions. E-waste management becomes an operational burden when you have to take into account different devices, local rules, distributed teams, and inconsistent processes.
Responsible e-waste management is no longer optional, it is a sustainability priority, and a core business responsibility.
The good news is, with the right strategy and a certified recycling partner, multi-location e-waste pickup becomes predictable, secure, and easy to manage.
What Is E-Waste Management?
E-waste management refers to the proper handling, collection, transportation, recycling, and disposal of electronic waste. This includes computers, laptops, phones, printers, cables, batteries, servers, and networking equipment.
It is a full lifecycle process. Devices are handled safely, data is protected, and materials are recovered in compliance with environmental standards. When done correctly, businesses reduce risk while supporting sustainability goals.
For a deeper look at reuse and recovery, see repurposed manufacturing.
Key Elements of E-Waste Management

- Collection and secure storage: Retired electronics are gathered and stored safely. Data-bearing devices require controlled access.
- Sorting and assessment: Devices are evaluated for reuse, refurbishment, resale, or specialized disposal.
- Data destruction: Drives and storage media are wiped or destroyed using verified methods. Learn more about data destruction.
- Recycling and material recovery: Valuable materials like copper, gold, aluminum, glass, and plastics are recovered. See upcycling and reuse.
- Responsible disposal: Non-recyclable components are disposed of using certified, environmentally safe methods.
- Compliance and reporting: Certified recyclers provide documentation for audits, ESG reporting, and regulatory compliance.
Why Multi-Location Businesses Need E-Waste Pickup
Retail chains, corporate offices, healthcare networks, and distributed teams all generate e-waste across locations. Managing electronics from multiple branches without a unified process creates risk and inefficiency.
Securely disposing of electronics across locations is difficult without a certified partner and a consistent strategy.
- Logistical complexity: Coordinating pickups across locations can lead to delays and unsafe storage.
- Data security risk: Laptops, servers, and drives often contain sensitive data. Without secure handling, breach risk increases. Certified partners provide verified data destruction.
- Compliance challenges: E-waste laws vary by state. Businesses operating nationwide must comply where devices are located.
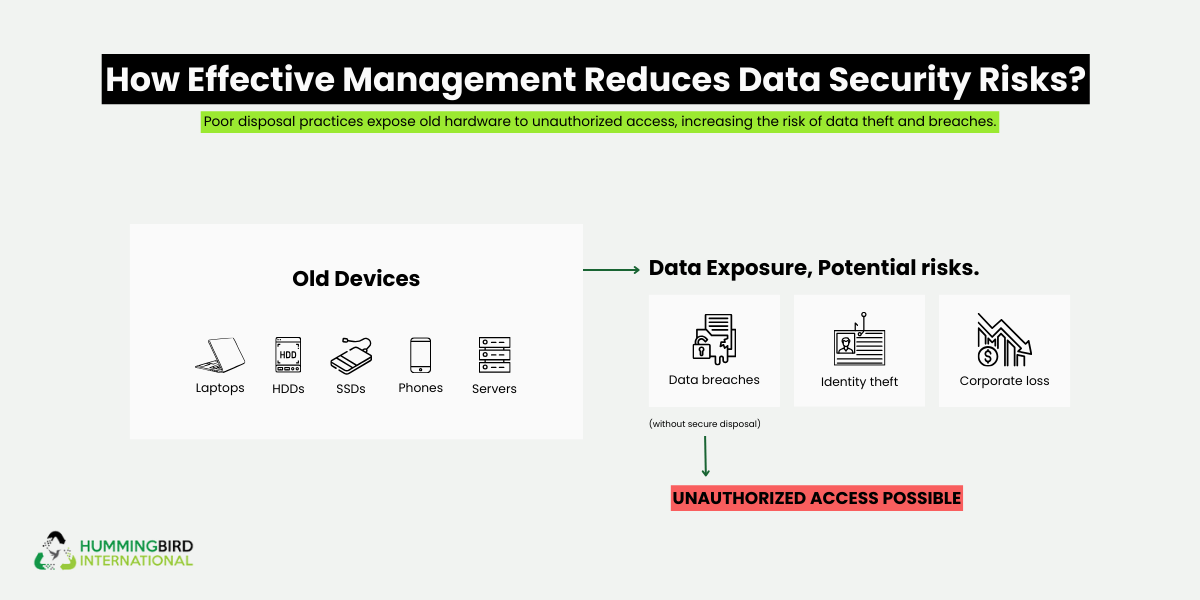
Compliance Across States
E-waste regulations differ by state. The safest approach is to use certified recyclers and maintain clear documentation for every pickup.
| State | Key Requirements | What Businesses Should Do |
| California | CEW program, landfill bans, approved recyclers | Use CalRecycle-listed partners and retain manifests |
| New York | Electronic Equipment Recycling & Reuse Act | Use certified recyclers and keep destruction certificates |
| Washington | E-cycle Washington landfill bans | Route devices through approved channels |
| New Jersey | Landfill ban for covered electronics | Ensure devices enter certified recycling streams |
ESG and Sustainability Reporting
Companies with ESG goals need accurate, location-wide recycling data. A multi-location program provides unified documentation, reduces risk, and strengthens brand credibility.
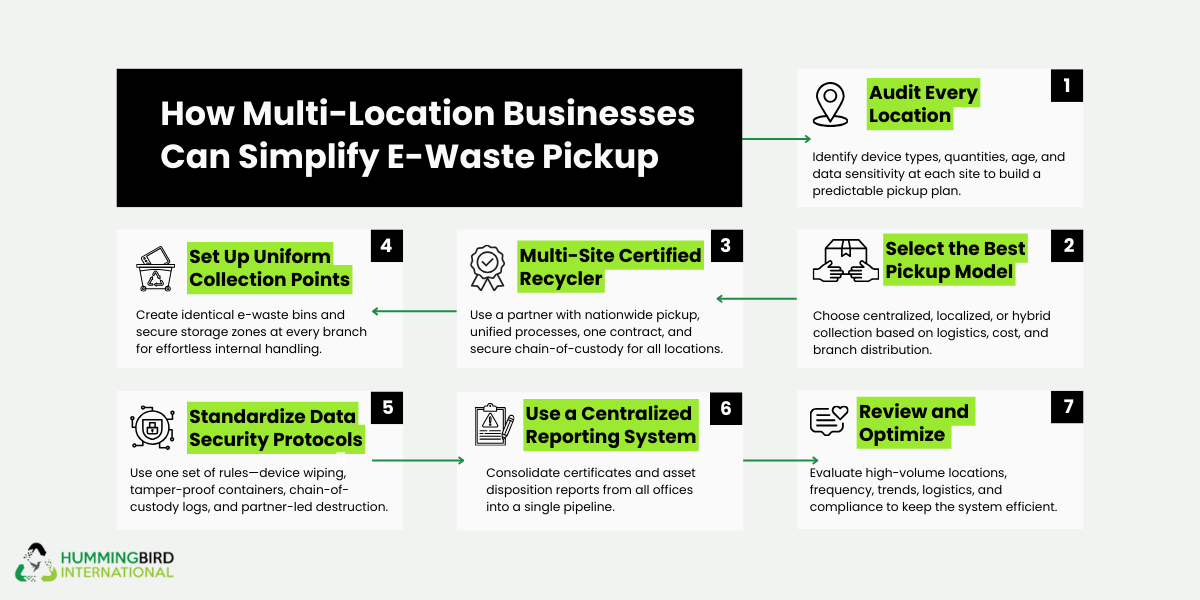
How to Simplify E-Waste Pickup for Multi-Location Businesses
The most effective programs are predictable, standardized, and centrally managed. The steps below help businesses scale e-waste pickup without friction.
Schedule an E-Waste Pickup
-
Conduct a Multi-Site E-Waste Audit
Start by identifying the type, volume, and condition of devices at each location. This includes laptops, servers, monitors, POS systems, and batteries. Tracking this data prevents surprises and supports accurate scheduling.
-
Choose the Right Pickup Model
Businesses typically use a centralized, localized, or hybrid pickup model. A certified ITAD partner can help select the most cost-effective option.
-
Work With a Certified Recycler
Certified recyclers provide standardized processes, documented chain of custody, and verified data destruction. See R2v3 certification for an example.
-
Standardize Internal Collection Points
Use the same labeled bins and secure storage rules at every site. This reduces training time and prevents improper handling.
-
Define Company-Wide Data Security Protocols
Standard data rules across locations eliminate confusion and reduce breach risk. Learn how certified handling works in secure device processing.
-
Centralize Reporting and Documentation
Unified reports, recycling certificates, and destruction records support audits, ESG reporting, and internal reviews. Reference certification standards.
-
Review and Optimize Over Time
Annual or biannual reviews help adjust pickup frequency, reduce costs, and maintain compliance as the business grows.
Benefits of Multi-Location E-Waste Pickup
- Stronger ESG performance through accurate diversion and recycling data
- Lower data security risk with verified destruction and tracking
- Operational efficiency from predictable workflows
- Cost control through consolidated vendors and pricing
- Improved brand trust with customers and stakeholders
Make Multi-Location E-Waste Pickup Simple
Managing e-waste across offices does not have to be complex. With standardized processes and a certified partner, businesses gain control, visibility, and peace of mind.
Schedule an E-Waste Pickup
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should multi-location businesses schedule e-waste pickups?
Most businesses schedule quarterly or biannual pickups. Tech-heavy organizations may need monthly service.
What electronics are accepted?
Certified recyclers accept computers, laptops, monitors, printers, networking equipment, phones, cables, and batteries.
How is data kept secure?
Through secure storage, chain-of-custody tracking, and certified data wiping or destruction with documentation.
Is one recycler cheaper than many local vendors?
Yes. A single recycler reduces administrative work, lowers risk, and supports volume-based pricing.


Leave a Reply